I’ve used for years the registry key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management to set a custom pagefile configuration on a server or a computer whenever required.
PowerShell can also be used to set the pagefile configuration. The Microsoft All-In-One Script members published on the Technet gallery a Script to configure virtual memory page file size (PowerShell)
The old fashioned way with the WMI commandline utility is another option. See for example: http://marckean.wordpress.com/2012/09/26/windows-server-2012-hyper-v-server-command-line-configuration-2/
However I don’t recommend to use the WMI Win32_Pagefile class on Windows Server 2012 because it’s deprecated.
([wmiclass]'Win32_PageFile').GetText("MOF")

Let’s try to discover how to set it without the Win32_Pagefile WMI class. We can start enumerating other WMI classes that have the occurence of the word “pagefile” in their name:
Get-CimClass -ClassName *PageFile*

We can list all the properties of the Win32_PageFileUsage WMI class:
Get-CimInstance Win32_PageFileUsage | fl *

The Allocatedbasesize property (768 in my example) is actually the size of the page file on the disk expressed in MB:
(Get-ChildItem c:\ -Attributes H,S | ? Name -eq "pagefile.sys").Length /1MB

You should also be aware that by default, the pagefile is
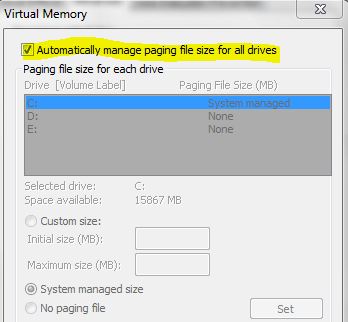
and this flag is actually a property of the Win32_ComputerSystem WMI class.
gwmi Win32_ComputerSystem | fl AutomaticManagedPagefile Get-CimInstance CIM_ComputerSystem | gm -Name AutomaticManagedPagefile

As you can see in the above picture, this flag can be written. For sure, Powershell will allow us to configure the pagefile using WMI or CIM.
Now that we can foresee how to set it, let’s try to figure out how much to set. Finding the appropriate guidance is the most difficult part and I’ll prove it.
The Windows XP recommendation that you can find on this page
For best performance, do not set the initial size to less than the minimum recommended size under Total paging file size for all drives. The recommended size is equivalent to 1.5 times the amount of RAM on your system.
has been erected as a somehow immutable law. Even if the Microsoft All-In-One Script members powershell script uses it, it doesn’t hold true anymore.
For XP and Windows 2003 server, there’s the following KB article, How to determine the appropriate page file size for 64-bit versions of Windows http://support.microsoft.com/kb/889654
Important Supportability Information: This article is specifically for computers that do not need kernel mode or full memory dump analysis. For business-critical servers where business processes require to server to capture physical memory dumps for analysis, the traditional model of the page file should be at least the size of physical ram plus 1 MB, or 1.5 times the default physical RAM. This makes sure that the free disk space of the operating system partition is large enough to hold the OS, hotfixes, installed applications, installed services, a dump file, and the page file. On a server that has 32 GB of memory, drive C may have to be at least 86 GB to 90 GB. This is 32 GB for memory dump, 48 GB for the page file (1.5 times the physical memory), 4 GB for the operating system, and 2 to 4 GB for the applications, the installed services, the temp files, and so on. Remember that a driver or kernel mode service leak could consume all free physical RAM. Therefore, a Windows Server 2003 x64 SP1-based server in 64-bit mode with 32GB of RAM could have a 32 GB kernel memory dump file, where you would expect only a 1 to 2 GB dump file in 32-bit mode. This behavior occurs because of the greatly increased memory pools.
For Windows 2008 and 2008 R2 servers, there’s the following KB article: How to determine the appropriate page file size for 64-bit versions of Windows Server 2008 and or Windows 2008 R2 http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2021748
See the Table 2. Default Page File Sizes for Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2.
Source: “Windows Internals” 5th edition Chapter 9: Memory Management Page 781.
There is no specific recommendation for page file size. Your requirements will be based on the hardware and software that you use and the load that you put on the computer.
Note Page file use should be tracked periodically. When you increase the use or the load on the system, you generally increase the demand for virtual address space and page file space.
To determine the approximate minimum page file that is required by your system, calculate the sum of peak private bytes that are used by each process on the system. Then, subtract the amount of memory on the system.
To determine the approximate maximum page file space that is required for your system, calculate the sum of peak private bytes that are used by each process on the system. Then, add a margin of additional space. Do not subtract the amount of memory on the system. The size of the additional margin can be adjusted based on your confidence in the snapshot data that is used to estimate page file requirements.
..and there’s the same “supportability” notice as the one for XP/2003.
Let me also mention 3 other sources:
- Best Practices for Setting Up Page File and Minimum Drive Size Required for OS Partition on Windows Servers by Santosh Bhandarkar, a MSFT partner.
- Pushing the Limits of Windows: Virtual Memory by Mark Russinovich
- Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012: Automatic Memory Dump by the Windows Server Core Team
How Big Should I Make the Paging File?
Perhaps one of the most commonly asked questions related to virtual memory is, how big should I make the paging file? There’s no end of ridiculous advice out on the web and in the newsstand magazines that cover Windows, and even Microsoft has published misleading recommendations. Almost all the suggestions are based on multiplying RAM size by some factor, with common values being 1.2, 1.5 and 2. Now that you understand the role that the paging file plays in defining a system’s commit limit and how processes contribute to the commit charge, you’re well positioned to see how useless such formulas truly are.
Since the commit limit sets an upper bound on how much private and pagefile-backed virtual memory can be allocated concurrently by running processes, the only way to reasonably size the paging file is to know the maximum total commit charge for the programs you like to have running at the same time. If the commit limit is smaller than that number, your programs won’t be able to allocate the virtual memory they want and will fail to run properly.
Confused? Let’s experiment and mess with it.
If I disable the pagefile, I’ve got the following warning:

Note that the amount of required RAM may vary.

After a reboot, there’s a second warning saying:

The temporary pagefile created on the disk is around 1GB.
Let’s fix this with the following code, a fork of the script from the Microsoft All-In-One Script members published on the Technet gallery
#Requires -Version 3.0
Function Set-PageFile {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Set-PageFile is an advanced function which can be used to adjust virtual memory page file size.
.DESCRIPTION
Set-PageFile is an advanced function which can be used to adjust virtual memory page file size.
.PARAMETER <InitialSize>
Setting the paging file's initial size.
.PARAMETER <MaximumSize>
Setting the paging file's maximum size.
.PARAMETER <DriveLetter>
Specifies the drive letter you want to configure.
.PARAMETER <SystemManagedSize>
Allow Windows to manage page files on this computer.
.PARAMETER <None>
Disable page files setting.
.PARAMETER <Reboot>
Reboot the computer so that configuration changes take effect.
.PARAMETER <AutoConfigure>
Automatically configure the initial size and maximumsize.
.EXAMPLE
C:\PS> Set-PageFile -InitialSize 1024 -MaximumSize 2048 -DriveLetter "C:","D:"
Execution Results: Set page file size on "C:" successful.
Execution Results: Set page file size on "D:" successful.
Name InitialSize(MB) MaximumSize(MB)
---- --------------- ---------------
C:\pagefile.sys 1024 2048
D:\pagefile.sys 1024 2048
E:\pagefile.sys 2048 2048
.LINK
Get-WmiObject
http://technet.microsoft.com/library/hh849824.aspx
#>
[cmdletbinding(SupportsShouldProcess,DefaultParameterSetName="SetPageFileSize")]
Param
(
[Parameter(Mandatory,ParameterSetName="SetPageFileSize")]
[Alias('is')]
[Int32]$InitialSize,
[Parameter(Mandatory,ParameterSetName="SetPageFileSize")]
[Alias('ms')]
[Int32]$MaximumSize,
[Parameter(Mandatory)]
[Alias('dl')]
[ValidatePattern('^[A-Z]$')]
[String[]]$DriveLetter,
[Parameter(Mandatory,ParameterSetName="None")]
[Switch]$None,
[Parameter(Mandatory,ParameterSetName="SystemManagedSize")]
[Switch]$SystemManagedSize,
[Parameter()]
[Switch]$Reboot,
[Parameter(Mandatory,ParameterSetName="AutoConfigure")]
[Alias('auto')]
[Switch]$AutoConfigure
)
Begin {}
Process {
If($PSCmdlet.ShouldProcess("Setting the virtual memory page file size")) {
$DriveLetter | ForEach-Object -Process {
$DL = $_
$PageFile = $Vol = $null
try {
$Vol = Get-CimInstance -ClassName CIM_StorageVolume -Filter "Name='$($DL):\\'" -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to find the DriveLetter $DL specified"
return
}
if ($Vol.DriveType -ne 3) {
Write-Warning -Message "The selected drive should be a fixed local volume"
return
}
Switch ($PsCmdlet.ParameterSetName) {
None {
try {
$PageFile = Get-CimInstance -Query "Select * From Win32_PageFileSetting Where Name='$($DL):\\pagefile.sys'" -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to query the Win32_PageFileSetting class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
If($PageFile) {
try {
$PageFile | Remove-CimInstance -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to delete pagefile the Win32_PageFileSetting class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
} Else {
Write-Warning "$DL is already set None!"
}
break
}
SystemManagedSize {
Set-PageFileSize -DL $DL -InitialSize 0 -MaximumSize 0
break
}
AutoConfigure {
$TotalPhysicalMemorySize = @()
#Getting total physical memory size
try {
Get-CimInstance Win32_PhysicalMemory -ErrorAction Stop | ? DeviceLocator -ne "SYSTEM ROM" | ForEach-Object {
$TotalPhysicalMemorySize += [Double]($_.Capacity)/1GB
}
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to query the Win32_PhysicalMemory class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
<#
By default, the minimum size on a 32-bit (x86) system is 1.5 times the amount of physical RAM if physical RAM is less than 1 GB,
and equal to the amount of physical RAM plus 300 MB if 1 GB or more is installed. The default maximum size is three times the amount of RAM,
regardless of how much physical RAM is installed.
If($TotalPhysicalMemorySize -lt 1) {
$InitialSize = 1.5*1024
$MaximumSize = 1024*3
Set-PageFileSize -DL $DL -InitialSize $InitialSize -MaximumSize $MaximumSize
} Else {
$InitialSize = 1024+300
$MaximumSize = 1024*3
Set-PageFileSize -DL $DL -InitialSize $InitialSize -MaximumSize $MaximumSize
}
#>
$InitialSize = (Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_PageFileUsage).AllocatedBaseSize
$sum = $null
(Get-Counter '\Process(*)\Page File Bytes Peak' -SampleInterval 15 -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).CounterSamples.CookedValue | % {$sum += $_}
$MaximumSize = ($sum*70/100)/1MB
if ($Vol.FreeSpace -gt $MaximumSize) {
Set-PageFileSize -DL $DL -InitialSize $InitialSize -MaximumSize $MaximumSize
} else {
Write-Warning -Message "Maximum size of page file being set exceeds the freespace available on the drive"
}
break
}
Default {
if ($Vol.FreeSpace -gt $MaximumSize) {
Set-PageFileSize -DL $DL -InitialSize $InitialSize -MaximumSize $MaximumSize
} else {
Write-Warning -Message "Maximum size of page file being set exceeds the freespace available on the drive"
}
}
}
}
# Get current page file size information
try {
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_PageFileSetting -ErrorAction Stop |Select-Object Name,
@{Name="InitialSize(MB)";Expression={if($_.InitialSize -eq 0){"System Managed"}else{$_.InitialSize}}},
@{Name="MaximumSize(MB)";Expression={if($_.MaximumSize -eq 0){"System Managed"}else{$_.MaximumSize}}}|
Format-Table -AutoSize
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to query Win32_PageFileSetting class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
If($Reboot) {
Restart-Computer -ComputerName $Env:COMPUTERNAME -Force
}
}
}
End {}
}
Function Set-PageFileSize {
[CmdletBinding()]
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory)]
[Alias('dl')]
[ValidatePattern('^[A-Z]$')]
[String]$DriveLetter,
[Parameter(Mandatory)]
[ValidateRange(0,[int32]::MaxValue)]
[Int32]$InitialSize,
[Parameter(Mandatory)]
[ValidateRange(0,[int32]::MaxValue)]
[Int32]$MaximumSize
)
Begin {}
Process {
#The AutomaticManagedPagefile property determines whether the system managed pagefile is enabled.
#This capability is not available on windows server 2003,XP and lower versions.
#Only if it is NOT managed by the system and will also allow you to change these.
try {
$Sys = Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
}
If($Sys.AutomaticManagedPagefile) {
try {
$Sys | Set-CimInstance -Property @{ AutomaticManagedPageFile = $false } -ErrorAction Stop
Write-Verbose -Message "Set the AutomaticManagedPageFile to false"
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to set the AutomaticManagedPageFile property to false in Win32_ComputerSystem class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
}
# Configuring the page file size
try {
$PageFile = Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_PageFileSetting -Filter "SettingID='pagefile.sys @ $($DriveLetter):'" -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to query Win32_PageFileSetting class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
If($PageFile){
try {
$PageFile | Remove-CimInstance -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Failed to delete pagefile the Win32_PageFileSetting class because $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
}
try {
New-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_PageFileSetting -Property @{Name= "$($DriveLetter):\pagefile.sys"} -ErrorAction Stop | Out-Null
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa394245%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_PageFileSetting -Filter "SettingID='pagefile.sys @ $($DriveLetter):'" -ErrorAction Stop | Set-CimInstance -Property @{
InitialSize = $InitialSize ;
MaximumSize = $MaximumSize ;
} -ErrorAction Stop
Write-Verbose -Message "Successfully configured the pagefile on drive letter $DriveLetter"
} catch {
Write-Warning "Pagefile configuration changed on computer '$Env:COMPUTERNAME'. The computer must be restarted for the changes to take effect."
}
}
End {}
}

How to determine the appropriate page file size for 64-bit versions of Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2860880/en-us
there is issue with settin up pagefile with .NET 4.5.2, it works with .NET 4.5.1 thou.
Do you mean there’s a problem with the code in the above blog post when you’ve .Net 4.5.2 installed?
yes,
“Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_PageFileSetting -Filter “SettingID=’pagefile.sys @ $($DriveLetter):'” -ErrorAction Stop | Set-CimInstance -Property @{
InitialSize = $InitialSize ;
MaximumSize = $MaximumSize ;
}”
returns error “Value out of range”
I have managed to make it work installing 4.5.2 dev kit, clean 4.5.2 ends with error
Ok, thanks for reporting the issue and narrowing it down to the exact code that fails 🙂
Last question, I’d like to know what operating system and PowerShell version you ran to get this error.
If I’d like to reproduce it, I need to know that.
Can you please post the result of a $PSVersionTable?
Thanks
/Emin